1. Introduction
Now that you have completed our beginner tutorial, whose result is a functional order management application, we’ll now focus on advanced behaviour modeling, using native and external APIs, and an introduction to data analysis elements Lists, Queries and Dashboards.
In 3. Advanced Behaviours area, we will explore how to communicate with OMNIA’s native API, in order to improve the user experience, and an External API. As a external API, Discogs was chosen for this example.
In point 4. Data analysis, we will explore how to model new lists and how to create dashboards on OMNIA.
2. Prerequisites
This tutorial assumes that you have created a OMNIA tenant and are logged in as a user with modeling privileges to this tenant.
It is necessary to have completed the steps in the Beginner tutorial, as this tutorial builds upon it.
3. Advanced Behaviours
Native API
-
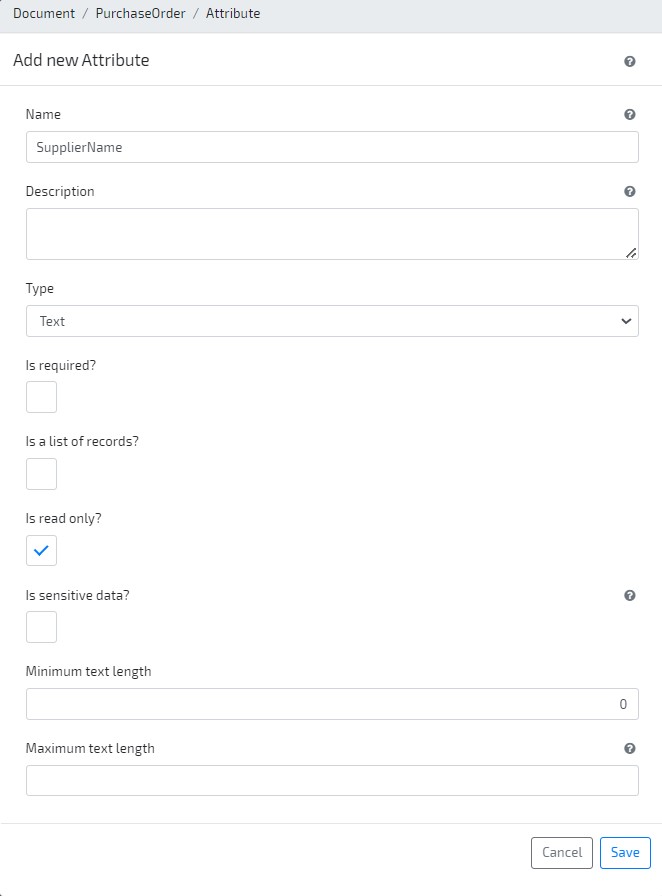
Go to the Modeler and edit the previously modeled document PurchaseOrder. Create a new Attribute by clicking the button Add new / Primitive on the top right side, and setting its Name and Type to SupplierName and Text, respectively. Set the attribute as Read Only.
-
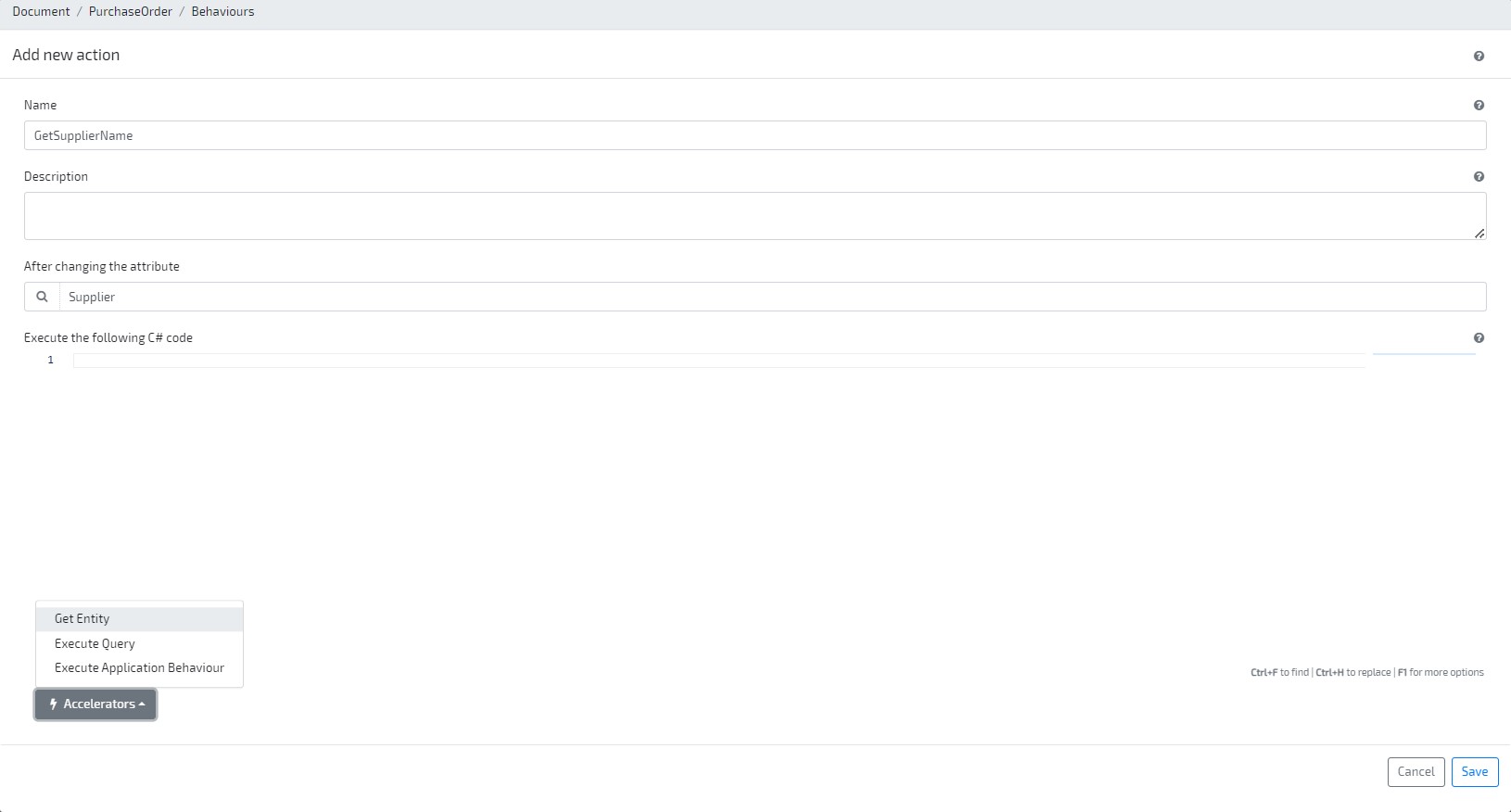
Create a new Action Behaviour to fill the new attribute (on the PurchaseOrder document, go to tab Entity Behaviours and click on Add new / (Action / Change)). Now let’s use one of our development “Accelerators” to get our SupplierName from the Agents attribute “_name”. Set its name GetSupplierName, and Supplier as the attribute that triggers the behaviour:
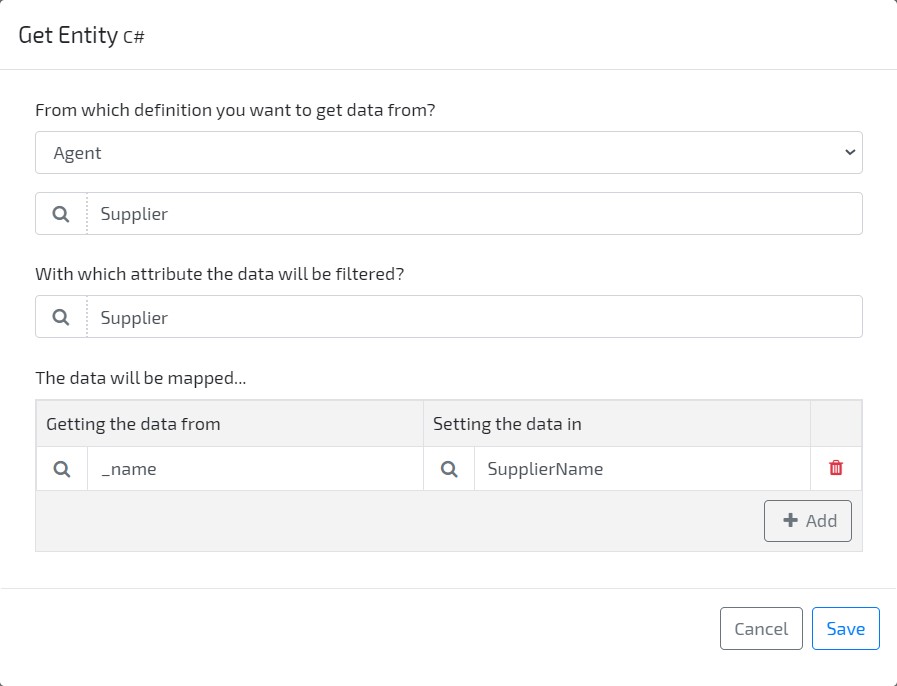
The output of the Get Entity C# accelerator should be as follow:
// Code generated by an accelerator (you can change it if you need) // The following code invokes the API to retrieve the data of an entity and set the values in the current entity if(string.IsNullOrEmpty(this.Supplier?.ToString())) return; // In order to prevent to invoke the API if the values were sent by the user if( this._Dto.HasPropertyChanged(nameof(this.SupplierName)) ) return; var httpClient = this._Context.CreateApplicationHttpClient(); var dataSource = "Default"; var requestResult = httpClient.GetAsync($"Supplier/{dataSource}/{this.Supplier}").GetAwaiter().GetResult(); if (!requestResult.IsSuccessStatusCode) throw new Exception($"Can't retrieve the entity '{this.Supplier}'"); var entity = requestResult.Content.ReadAsAsync<SupplierDto>().GetAwaiter().GetResult(); this.SupplierName = entity._name; -
Build & Deploy model
-
Go to Application area, and create a new PurchaseOrder document. Observe that, when Supplier is identified, the SupplierName is automatically retrieved.
External API
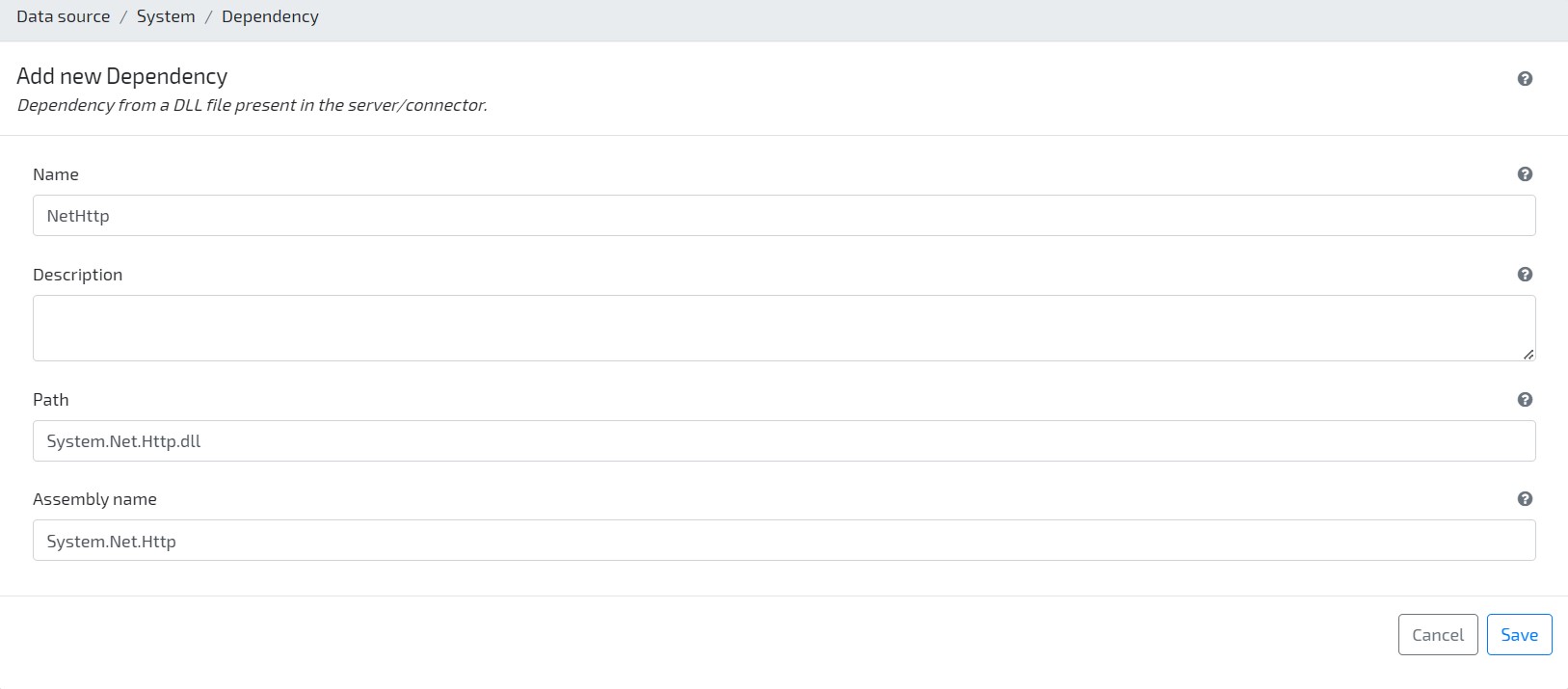
- Go to the Modeler and click on option Business / Data sources / System to add references to this data source. Click on button Add new > File Dependency to add a new Behaviour Dependency for .NET assembly System.Net.Http
-
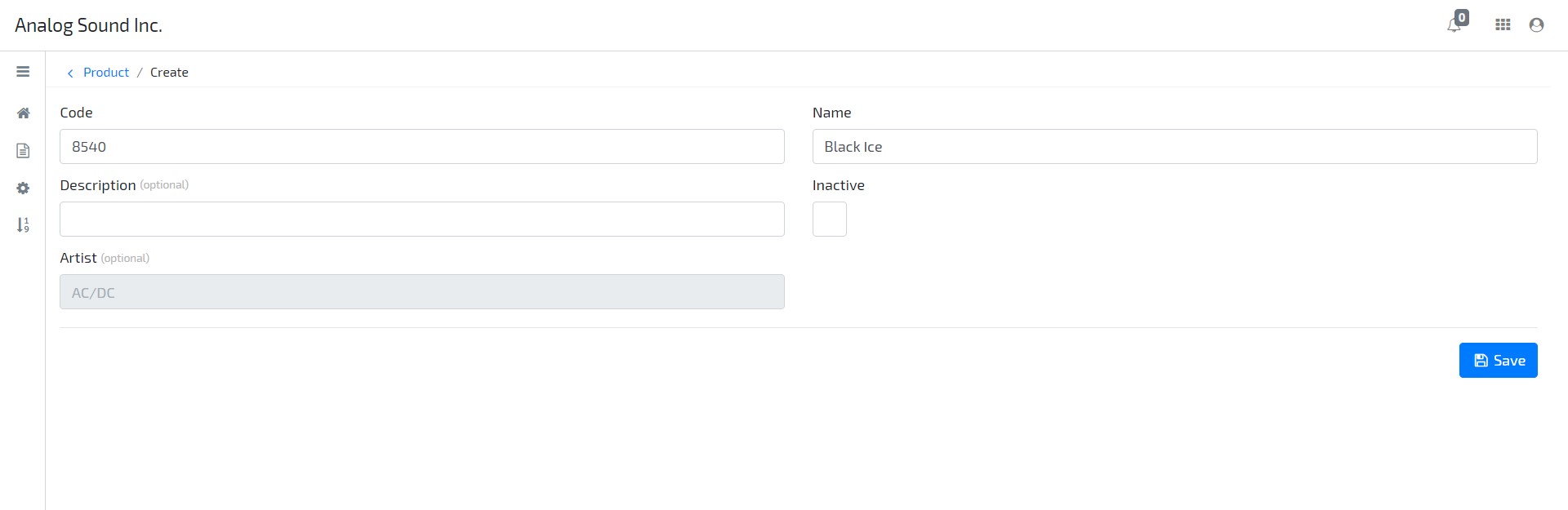
Edit the previously modeled resource Product. Create a new Attribute by clicking the button Add new / Primitive on the top right side, and setting its Name and Type to Artist and Text, respectively. Set the attribute as Read Only.
-
Navigate to tab Behaviour Namespaces and add namespace System.Net.Http
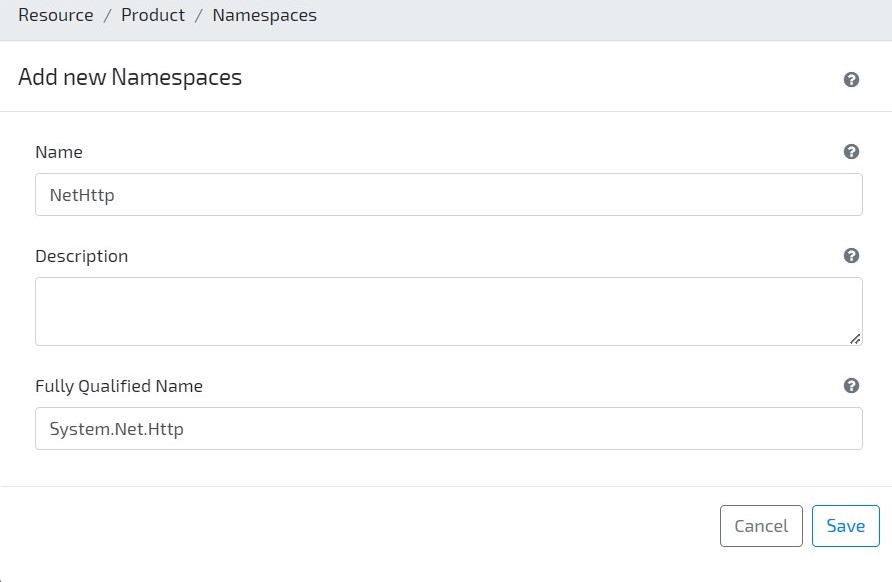
-
Create a new Action Behaviour to fill the new attribute (go to tab Entity Behaviours and click on Add new / Action). Set GetRecordData as Name, _code as the attribute that triggers the behaviour, and paste the following code:
var client = new HttpClient() {DefaultRequestHeaders = {}}; client.DefaultRequestHeaders.Add("User-Agent", "OMNIA"); string apiEndpoint = $"https://api.discogs.com/masters/{_code}"; var requestResult = client.GetAsync(apiEndpoint).GetAwaiter().GetResult(); string responseBody = requestResult.Content.ReadAsStringAsync().GetAwaiter().GetResult(); Dictionary<string, object> responseDictionary = JsonConvert.DeserializeObject<Dictionary<string, object>>(responseBody); if (!requestResult.IsSuccessStatusCode) throw new Exception($"Error on retrieving data from Discogs API: {responseDictionary["message"].ToString()} {apiEndpoint}"); _name = responseDictionary["title"].ToString(); if (responseDictionary.ContainsKey("artists")) { Newtonsoft.Json.Linq.JArray artists = (Newtonsoft.Json.Linq.JArray)responseDictionary["artists"]; if (artists != null && artists.Count > 0) { Artist = artists[0]["name"].ToString(); } } -
Build & Deploy model
-
Go to Application area, and create a new Product resource. Observe that, when Code is identified (e.g. try with value 8540), the Name and Artist is automatically retrieved.
4. Data Analysis
Queries and Lists
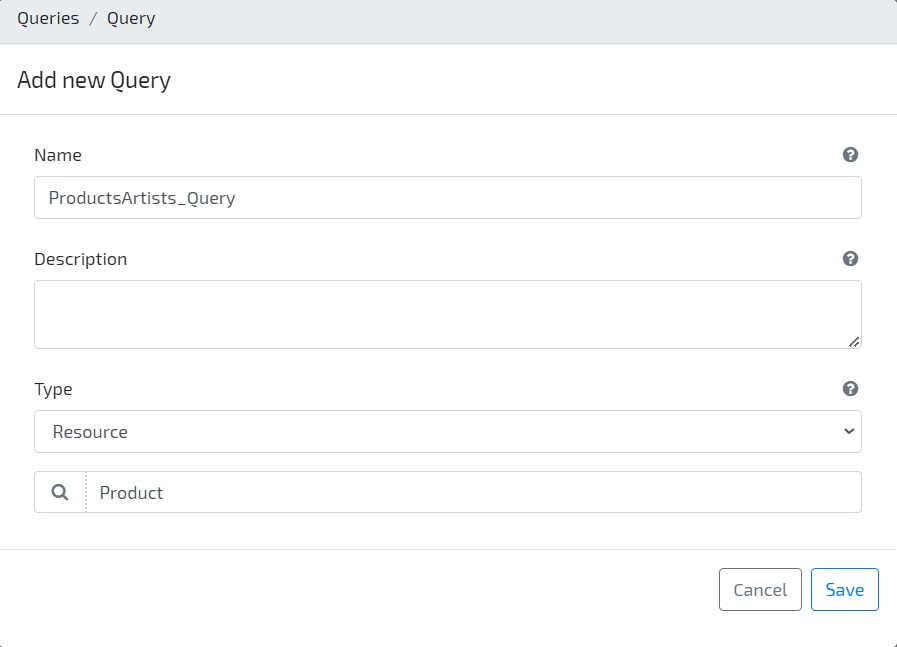
- On your Modeler area, go to Query / Queries and click on button Add New to create a new query. Set ProductsArtists_Query as Name and Resource / Product as Type.
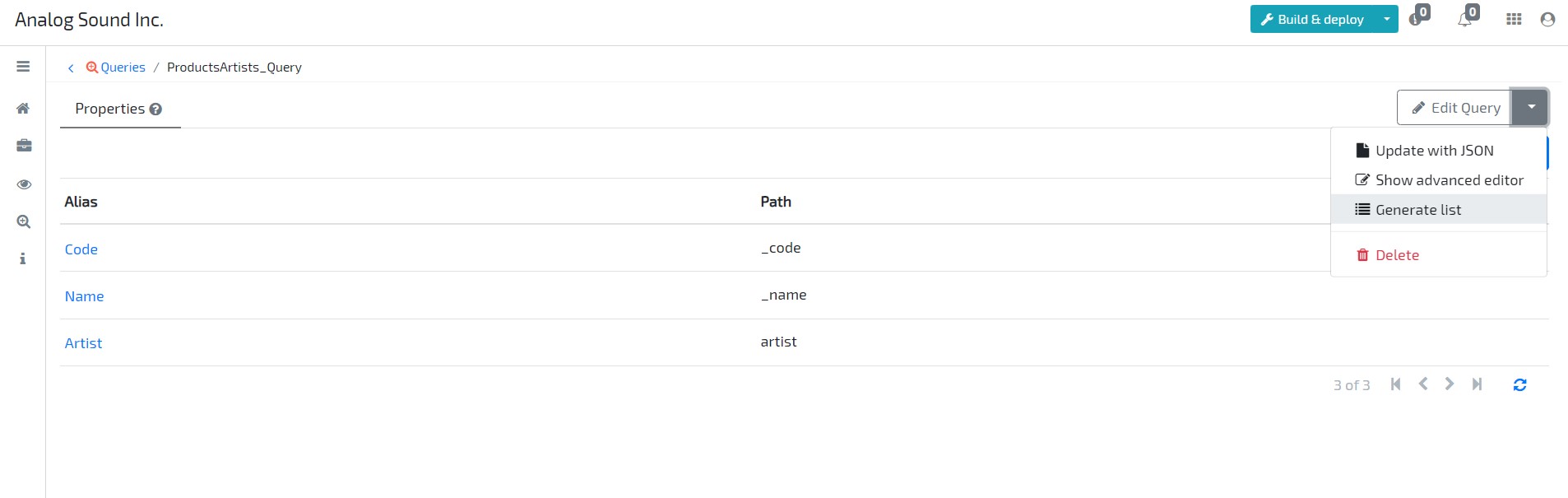
- Now open your query and click on Add New to add columns to it. Add a column with Alias Code and Path _code.
-
Repeat previous step to add columns with alias Name and Artist, whose Path is _name and artist, respectively.
- On top right side, click on button More options / Generate list to create a new list based on the given query.
Dashboards
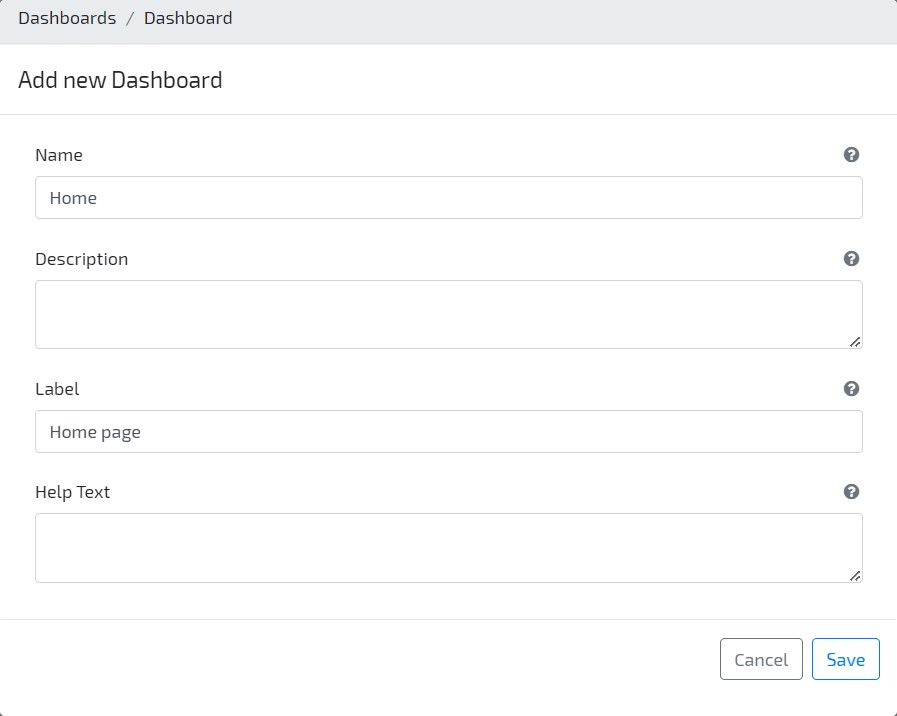
- On your Modeler area, go to User Interface / Dashboards and click on button Add New to create a new dashboard. Set Home as Name, so that the dashboard is visible on application’s homepage.
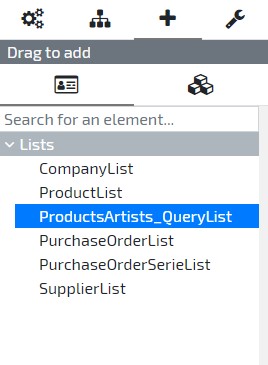
- On the right sidebar select the third tab, identifiable by the + sign, and then select the first tab below. Verify there is a ProductsArtists_QueryList option listed. Press and hold down the list then drop it into the Home Dashboard.
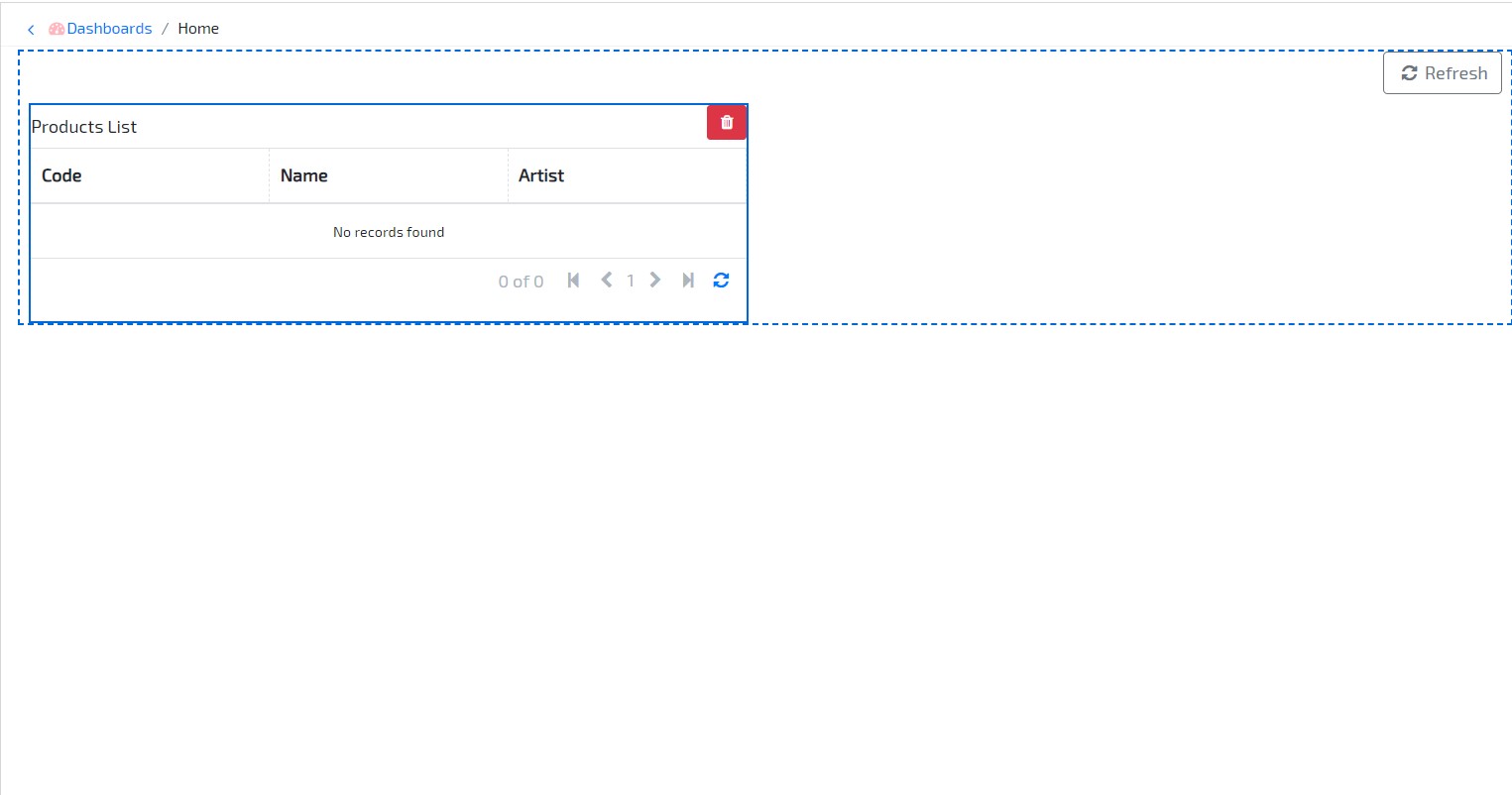
- Click on the list and change its Label to Products List and Size to 6. Don’t forget to save your changes.
-
Build & Deploy the model.
-
Go to the application and check the homepage dashboard. Data for the products you have created will be visible.