1. Introduction
In OMNIA Platform Pages you can manage entity instances, list records, or do something completely different.
This feature allows you to model as many pages as you want in your applications. Unlike Forms, Pages are not necessarily associated to an entity.
Pages are composed by a set of Elements. Each element references a Component. Click here to learn more about them.
2. Pages Structure
On a modeler perspective, a Page is composed by the following definitions:
Variables
Each page can have its own set of Variables. The purpose of the Variables is to temporarily store the page state (data relevant to the page usage).
A Variable value can be read or set at anytime while interacting with the page.
As an example, variables can be used to store the Url to redirect when exiting the page, or to set a flag that controls a loader to be shown when something is processing and users must wait for it to end.
Url Parameters
A Url Parameter is the definition of data that will be sent to the Page as a part of its URL.
As an example, given the following Url:
https://www.example.com/widgets?color=blue&size=large
We have two Url parameters to define in our page: color and size.
Unlike Variables, a Url parameter value is automatically set from the Url used to access the page. The value can be read but not changed.
Refs
Refs are responsible by exposing Outbound Component attributes so their value can be used on a Page.
They are available to be used on code expressions and on Page/Page Elements configuration, by binding the Ref as the source of the value for that attribute.
Behaviours
OMNIA Platform Pages only have one behaviour available: Initialize.
As on other modeling features like Forms or Dashboards, this Behaviour will be executed when accessing the page.
Other Behaviours that are usually available (e.g. Formula, On Change, Before Save) should now be implemented on each page Element. Each Element references a Component that itself makes available a set of Events.
A behaviour code expression is transformed into a JavaScript function. These functions can have two possible signatures:
- Page Behaviour
initialize({ context, variables, urlParameters, refs }) {
//add your code here
}
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| context | This property contains information about the current user and the operation being made |
| variables | The values of the variables modeled on the page |
| urlParameters | The values of the Url parameters set when accessing the page |
| refs | The Outbound attribute values for each Component located on the page |
- Element Behaviour
_descriptionInput_OnChange({ context, variables, urlParameters, refs, indexes, currentElement, currentIndex }, params){
//add your code here
}
Element Behaviours contains the properties available on Page Behaviours and adds four new properties.
Before we look at these new properties, it is important to highlight that properties indexes, currentElement and currentIndex only have value when the Behaviour is part of an Element located inside a forEach Component. This happens because these properties expose data related to a record inside collection being iterated by the forEach.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| indexes | This property contains the index of collection iterated by the forEach for the current element. If the collection is located within another, indexes of the parents are also included |
| currentElement | This property contains the data of the current entry inside the collection being iterated |
| currentIndex | This property contains the index of the current element inside the collection being iterated |
| params | A list of parameters exposed by the Component. Each Component exposes a set of parameters of different types for each Event |
Let’s evaluate an example of these properties in action. The scenario we’re using is composed by a document named PurchaseOrder, with a collection OrderLines. That collection itself has a nested collection, named OrderWarehouse.
- First level collection (OrderLines)
When we’re on a behaviour of a first level collection, the indexes property contains only one key named after the forEach element, orderLinesForEach:
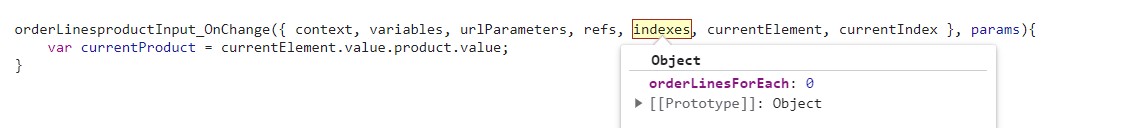
The property currentElement will contain the properties and the data of the orderLines element being iterated:
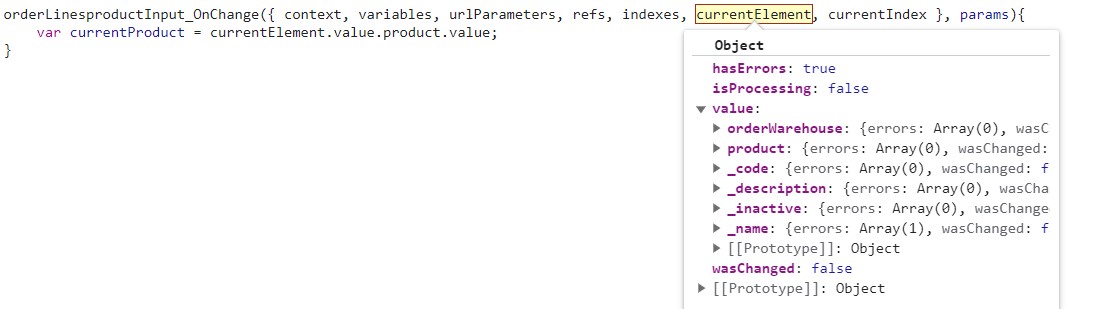
At last, the currentIndex is a integer that represents the position of the current element in the collection.
- Nested collection (OrderWarehouse)
When we’re on a behaviour of a nested collection, the indexes property contains multiple keys, one for each forEach element. In this scenario we’ll have two keys, orderLinesForEach and orderLinesorderWarehouseForEach:

The property currentElement will contain the properties and the data of the orderWarehouse element being iterated:

At last, the currentIndex has the same behaviour as in a first level collection.
With this information we have all we need to access the parent of the current element if necessary.
Scripts
Each page has a Scripts code area that can be used to define JavaScript functions to be used on multiple code expressions within the page.
The script is composed by a class named after the page. The custom code must be added inside this class.
class CompanyFormPageScripts {
showAlert(message) {
alert(message);
}
}
const companyFormPage = new CompanyFormPageScripts();
The developed functions can be called from any page code expression as follows:
companyFormPage.showAlert("Hello World!");
In addition to the page Scripts, it is also possible to use functions defined on the model Scripts.
Styles
CSS Styles can be used on pages to change the way it looks and behaves.
To add CSS Styles to a page, you can use the global CSS Styles described here, or add styles specific to the page being modeled.
Elements
When we are creating a Page, all the Elements a modeler can include on it reference a Component.
If we compare pages with Forms or Dashboards, our Elements based on Components can grant an additional level of flexibility, since we are not limited to use Omnia internal lists or inputs. We can create our own to ensure the best user experience.
Elements have a set of default properties that can be configured:
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| isHidden | Boolean that determines if the element is visible. Its value can be static, bound to a variable/ref or the result of a expression |
| groupElements | Boolean that determines if the element is grouped with its children. When elements are grouped, they behave as one in drag and drop operations. |
| classesStyles | The CSS Classes to be added to the rendered element. Available if configured o the component |
| cssStyle | The definition of CSS variable values of the selected element. Its value can be static, bound to a variable/ref or the result of a expression. Available if configured o the component |
3. Modeling Pages
When we are modeling a page, we’ll be using our Page Editor.
The editor is composed by two areas: a design/preview area, and a menu located on the right sidebar.
The menu is composed by five areas:
- Properties: The properties of the page or the currently selected page element.
- Elements Tree: The list of elements that compose the page, organized on a tree.
- Drag to add: The list of Components that can be dragged to the design/preview area.
- Variables: The list of page Variables. Includes options to add/remove variables
- Url Parameters: The list of page Url Parameters. Includes options to add/remove Url Parameters
- Configure view: Options to control the design/preview area. It is possible to show hidden elements, choose a Language to preview how its texts are applied, choose a Theme or activate Live Preview. When live preview is active, the modeling controls are removed from preview area.
How to add a new Page?
To add a new page go to the Modeling area, find the User Interface / Pages option on the menu and access it. This will take you to your Pages management dashboard.
Now select Add new and fill in the following information:
- Name: the name of the asset (needs to be unique within the model);
- Description: the textual explanation of the theme’s purpose (can be used as development documentation).
- Select a template: the template to be used as base when generating the page. Click here to see the available templates.
How to edit a Page?
By accessing User Interface / Pages in the sidebar and selecting one from the list.
You can not only change your Page design, but also generate the page again, based on a template.
How to add a variable?
On modeler, navigate to a page and on the right side menu open option Variables / Add variable.
Fill the following parameters:
- Name: the name of the Variable (needs to be unique within the Page);
- Description: the textual explanation of the Variable purpose (can be used as development documentation).
- Kind: the kind of the variable. Can be of type Primitive, an OMNIA definition (Agent, Resource, …) or a Component Type. These types are exposed by the component packages;
- Type: the type of the variable
- Is required value?: define if the variable must have a value;
- Is a list of records?: define if the variable contains more than one record of the given type;
- The initial value of the variable: the value the variable is initialized with. This parameter is only available for variables of Primitive kind. For variables of other Kinds, the initial value should be defined on Initialize Behaviour.
How to use a variable?
Variables can be used in a page in two different ways:
- Code Expressions
Variables can be accessed on Javascript code. They are available on variables object, and its value can be read or set.
function companyFormPage_Initialize({ context, variables, urlParameters, refs }, params) {
variables.myFirstVariable = "My variable value";
alert(variables.myFirstVariable);
}
- Binding
Variables can be bound to a page or Element attribute. When bound, the property value will be the same as the variable value.
To bind a variable with an element attribute, start by selecting the element on the preview area, and on the right side menu edit the intended attribute, set its value type to Binding and select the previously created variable.
How to add a Url Parameter?
On modeler, navigate to a page and on the right side menu open option Url Parameters / Add parameter.
Fill the following parameters:
- Name: the name of the Url Parameter (needs to be unique within the Page);
- Description: the textual explanation of the Url Parameter purpose (can be used as development documentation);
- Type: the type of the Url Parameter. It can be a Primitive type or an Object;
- Is a list of records?: define if the Url Parameter contains more than one record of the given type;
How to use a Url Parameter?
Url Parameters can be used in a page in two different ways:
- Code Expressions
Url Parameters can be used on Code Expressions within the page. They are available on urlParameters object.
function companyFormPage_Initialize({ context, variables, urlParameters, refs }, params) {
const codevalue = urlParameters.code;
}
- Binding
A Url Parameter can be bound to a page or Element property. When bound, the property value will be the same as the parameter value.
How to use a global script function?
On modeler, navigate to a page and access a Behaviour:
- Page: on the right side menu open option Properties/Behaviours;
- Element: select the element and on the right side menu the Behaviours list is available.
Given that we have a model Script with name Notifications and a function showAlert, we can call this function using the following code:
notification.showAlert("Hello World!");
See more about global scripts here.
How to add a page script?
On modeler, navigate to a page on the right side menu open option scripts.
A modal is opened with a code expression, where you can add your JavaScript code to be used inside the page.
How to use a global style?
On modeler, navigate to a page and on the right side menu open option Properties, and Styles area will be available.
To use a global style, simply introduce the CSS classes on property classesStyles.
How to add a page style?
On modeler, navigate to a page and on the right side menu open option Properties, and Styles area will be available.
You can add page specific styles by introducing them on property styles.These styles can then be used in the page or page elements.
How to add a Element to a page?
On modeler, navigate to a page and on the right side menu open option Drag to add.
On this menu option, you can find all internal Components along with Components imported from a package:
You can drag one to the Page preview area and drop it in the intended location. When the component is dropped, it is transformed into a page Element that references said Component, and you can change its configuration. Each Component exposes a different set of Attributes, Events and Styles that you can configure while modeling.
Focusing on Attributes and Styles, its value can be set in different ways:
| Value Source | Description |
|---|---|
| Direct | Value is set directly, with a static value |
| Binding | Value is bound with a variable, urlParameter or ref |
| Expression | Value is computed using a Javascript code expression. Since these expressions are executed on every render, the code must be simple and execute fast. |
| Asset | Value is selected from the list of model Assets |
| Translation | Value is selected from the list of model Translations |